New tools, whether in the form of better pharmaceutical products, more precise instrumentation or new technologies to assess various parameters of ocular health, seem to be in abundance this year at ARVO. As we gain in our knowledge of cornea and external disease, the results can only benefit our patients. Here are some of the ways that research is helping us reach that goal.
After a previous study showed that testosterone cream increased tear production in dry-eye patients based on Schirmer values, an investigator at Memphis' Southern College of Optometry recruited 20 patients with a decreased tear film breakup time (<10 seconds) and accompanying symptoms and assessed them with the Ocular Surface Disease Index. The patients applied 5% testosterone cream to their eyelids b.i.d. for three weeks, and the OSDI and TBUT were repeated. Included were 17 females and three males, mean age 45.8, range 22 to 65 years.
The baseline TBUT was 4.22 seconds with an OSDI score of 39.7, which corresponds to moderately severe dry eye. At three weeks, the TBUT increased to 6.02 seconds, and the OSDI score declined to 20.33, a mild rating based on OSDI. No patient showed an increased OSDI score after treatment, and most had a dramatically reduced OSDI score. OSDI changes were statistically significant; TBUT changes were not.2032
An oral dry-eye nutritional supplement was significantly more effective than placebo and has potential as a dry-eye treatment, says a study by Schepens Eye Institute and Ophthalmic Research Associates. The double-masked, randomized, controlled, parallel-group study evaluated dry-eye signs and symptoms as induced by the controlled adverse environment (CAE) test, which measures signs and symptoms before, during and following acute exacerbation. Following a three-week washout 24-dry eye patients were randomized to receive either the oral supplement or multivitamin placebo b.i.d, in conjunction with the same standard artificial tear product t.i.d. for 10 weeks. Ophthalmic examinations and follow-up CAE challenges took place at weeks three, six and 10, and 23 patients completed the study. Table 1 shows patient-reported symptom scores (0-4 on a standardized scale) during CAE exposure.2047
|
Table 1. Oral Dry-Eye Supplement vs. Multivitamin |
| Treatment | Baseline | p-value | Week-3 | p-value | Week-6 | p-value | Week-10 | p-value |
| Oral Supplement |
3.05 |
0.195 |
2.86 |
0.482 |
2.44 |
<0.0001 |
2.32 |
<0.0001 |
| Multivitamin (placebo) |
3.13 |
|
2.72 |
|
3.02 |
|
2.91 |
Though the labeling for cyclosporine A (Restasis, Allergan) indicates six months for full effectiveness, a study in Montana and the University of Pittsburgh suggests that patients report improvement in symptoms after only 30 days of therapy. The study enrolled 10 patients with a history of at least moderate dry-eye symptoms and evidence of corneal staining. For 30 days the subjects recorded how the cyclosporine A drops felt upon instillation, if their eyes felt better than when they started the drops, and how many times they thought about their eyes each day. Patients were also asked to rate, on a scale of 1 to 5 (5=great impact, and 1= no impact) how their dry eye impacted six types of daily activities.
After 30 days of therapy, patient scores improved for five of the measures (working, outdoor activities, watching TV, reading and driving). The improvement in ability/desire to participate in outdoor activities achieved statistical significance at days nine, 12 and 13. Most patients (67 percent) said their eyes felt better after 30 days than before starting treatment, and 60 percent found the drops to be soothing or only minimally stinging.2026
Dry Eye—Tears
Lipid layer thickness (LLT) has been correlated to tear evaporation, tear film stability, and other ocular signs. How does LLT correlate with symptoms of dry eye? A Harvard University group using a custom symptoms questionnaire that rates symptoms from 0 to 24 enrolled consecutive patients presenting for examination with a symptom score >5. A custom designed lipid-layer interferometer was used to quantify the LLT (OU), which was graded from 45 to 180 nm. LLT <60 nm was classified as thin and compromised, 75 nm as marginal, and >90 nm as adequate and thick.
Symptomatic subjects classified as moderate (n=41; symptom score 5 to 9 points, mean = 6.8), and severe (n=20; symptom score >10 points, mean =12.8). In the moderate group, 48.7 percent exhibited thin and compromised LLT, 36.5 percent, a moderate LLT, and 14.6 percent, an adequate LLT. In the severe group, 65 percent exhibited thin and compromised LLT, 25 percent, moderate LLT, and 10 percent, adequate LLT. In both groups the percentage of eyes with a LLT <60 nm was significantly higher than expected if no relationship existed between LLT and dry eye symptoms.
Patients with severe dry-eye symptoms revealed a higher frequency of reduced LLT compared to moderate patients, with 85.2 percent of the moderate and 90 percent of the severe group exhibiting thin or marginal LLT. However, since 14.6 percent of the moderate and 10 percent of the severe group exhibited adequate LLT, a thick lipid layer cannot guarantee the absence of dry-eye symptoms. A possible explanation is the recently reported correlation between dry-eye symptoms and the sign of lid wiper epitheliopathy in the absence of any positive conventional ocular signs. This study suggests the presence of dry-eye symptoms increases the likelihood of a thin or marginal lipid layer, and the need to consider the reason for the lack of an absolute correlation between dry- eye symptoms and LLT.4444
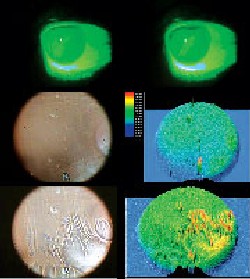
Tear breakup starts from the lipid film, much earlier than that detected by the conventional fluorescein method, say Miami researchers. TBU of the lipid film starts with lipid condensation followed by rapid thinning and rupture of the aqueous tear film.
In five healthy volunteers and five patients with lipid tear and aqueous tear deficiency (LTD/ATD), researchers at the Ocular Surface Center, Miami used an interference camera to perform kinetic analysis of tear interference images of the central 8 mm of the pre-corneal lipid tear film. Subjects held the blink until an unbearable discomfort occurred. The time (defined as non-invasive NTBUT), pattern and location of the lipid-film breakup were compared to that of the fluorescein-stained TBUT.
In all cases, NTBUT of the lipid film started significantly earlier than TBUT. In normal subjects, NTBUT was 7 ±1 second, while TBUT was 22 ±11.2 seconds. In LTD/ATD cases, NTBUT was 1.9 ±1.3 seconds, while TBUT was 3.9 ±0.6 seconds. NTBU started with condensation of lipids into thicker lipid spots or lines (formed between lipid waves) and evolved rapidly into thinning, resulting in a breakup of the lipid tear film. The location of NTBU of dots or lines occurred randomly between different blinks and corresponded well with ensuing fluorescein TBU pattern. The location tended to be in the region near the lower lid margin or the central cornea in normal subjects. In LTD/ ATD cases, the TBUT can be located in the upper, central or lower cornea.4439
Japanese investigators also used the interference camera to study the tear-film lipid layer in 90 eyes of 45 office workers who used computers more than two hours per day, and more than 40 hours per month. They assessed symptoms, tear interference grade, lipid layer thickness, fluorescein scores, tear breakup time and the meibom expressibility.
They found that 21 of 45 (46.7 percent) subjects had dry-eye symptoms. In DR-1 grading, 85 of 90 (94.4 percent) were grade 1 or 2, in which the average of the lipid layer thickness was 39.6 ±10.2 nm. Five of 90 (5.6 percent) were grade 3 or 4, with an average of the lipid layer thickness of 190.4 nm ±17.8 nm. The lipid layer thickness was decreased (<60 nm) in 82 of 90 (91.1 percent), and was abnormally increased in five of 90 (5.6 percent). In 72 of 90 (80 percent), BUT was shortened, and the average was 3.6 ±1.9 seconds. The average of the meibom expressibility score was 0.96 ±0.94.
The high rate of abnormalities in the tear film lipid layer suggests that tear lipid layer thickness affects the dry eye in VDT work, they conclude.4442
|
|
| A representative lipid tear deficiency and aqueous tear deficiency (LTD/ATD) patient. The measured tear breakup by fluorescein (A) and after (B) the tear film breaks. In the same case, a noninvasive TBUT measured by kinetic tear interferometry before (C) with corresponding elevation map (D) and after the tear film breaks (E). The corresponding elevation map (F) showing the tear film breaks in all areas of the cornea with higher peak intensity colors than in a normal subject. |
Allergy
Proving once again the connection between nasal and ocular allergy, a multicenter, open-label, crossover, three-visit, four-week study evaluated the impact on quality of life in rhinitis patients when topical ocular therapy is added to systemic and/or nasal medication regimens. Two QOL instruments, the RQLQ and ACQLQ served as evaluatory criteria at baseline and evaluation visits. Diagnosed rhinitis patients on stable doses of prescribed rhinitis treatment (nasal and/or systemic), which continued throughout study, were included. Prior medication regimens consisted of systemic antihistamine (~50 percent), antihistamine and nasal spray (33 percent), or nasal spray alone (16 percent). No patients were prior users of prescription ocular allergy therapy.
Allergic rhinitis patients experienced clinically and statistically significant improvements in QOL with addition of topical ophthalmic medication; this was most evident in ocular parameters of two different QOL tools, but was also evident globally, and in nasal symptom categories. The group advises that the ocular component of allergy, and the broad surface area the eye provides for the collection of allergens should not be overlooked when prescribing therapy regimens.94
Surgery
Investigators at the University of Texas in San Antonio explored the possibility of eliminating the thrombin component of the fibrin glue to simplify the technique of "sutureless" pterygium surgery. They tested the stability of the conjunctival autograft (CAG) following pterygium excisions that were secured solely with fibrin sealant alone. Their study included 28 eyes of 28 patients who underwent pterygium surgery with fibrin sealant application. No sutures were used in 17 eyes of 17 patients. Mean limbal dimension of the pterygia was 5.9 mm. Mean corneal extension was 3.84 mm; mean autograft size, 22.27 mm2; mean follow-up, 11.25 weeks. The CAGs were placed onto the scleral bed maintaining limbal orientation. The fibrin sealant component of the tissue adhesive was infused beneath the CAG and adjacent conjunctival margins without thrombin. All grafts adhered within 60 seconds.
Use of the fibrin sealant alone simplifies application since the solution is less viscous and allows several seconds for graft manipulation. In this series, there were no cases of graft loss or dehiscence, suggesting that the fibrin sealant component alone provides sufficient adhesive strength for autograft surgery. More extensive follow-up is needed to determine recurrence rates.954
Wilmer Institute researchers developed a series of novel biocompatible chondroitin sulfate-based tissue adhesives that permit controllable gelation without external energy input such as radiation or heat. The tissue adhesive is composed of chondroitin sulfate aldehyde (CS-ald) and polyvinylalcohol-covinylamine (PVA-A).
CS-ald and PVA-A were combined by mixing a 2:1 volume ratio of 30 percent CS-ald and 10 percent PVA-A. The adhesive was used immediately after mixing. The reaction starts immediately and completes in two to five minutes.
Fibroblasts were seeded onto tissue surfaces that had been treated with CS-ald solution (25 percent) for five minutes and co-cultured with the tissue adhesive for 14 days. Fluorescent assay demonstrated that cells remained viable and proliferate on the tissue adhesive. The tissue adhesive was used as sealant for protein (collagen)-abundant tissues, including the cornea. The measurable maximal gluing tensile strength was 40 kPa. This sealing strength is adequate for corneal incisions and is superior to sutures.4997
University of Iowa researchers sought to characterize wavefront aberrations in patients who underwent deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty, to compare these findings with the wavefront aberrations in PKP patients, and to determine if higher-order aberrations limit the final visual acuity in DLEK patients.
In another study, they conducted pre- and postop wavefront and topographic assessment on 40 consecutive DLEK patients. Five patients had a 9-mm incision DLEK, while 28 had a 5-mm incision DLEK. Six were converted to PKP and served as a comparison group.
Preliminary results show that the mean total RMS value (u) at six months was 0.514 in the 5-mm DLEK, 1.156 in the 9-mm DLEK, and 1.423 in the PKP groups, while the higher-order component was 0.197, 0.400, and 0.5455, respectively. Third-term coma was most commonly seen preoperatively in each group, consistent with central corneal thickening associated with Fuchs' dystrophy or bullous keratopathy. Over time, third-term trefoil was most commonly displayed. By six months, there was a return of third-term coma, but to a much lesser degree than preoperatively. Mean best-corrected Snellen vision at six months was 20/45 (5-mm DLEK) and 20/33 (9-mm DLEK and PKP).
DLEK induces fewer higher-order wavefront aberrations than PKP, though this does not translate into improved Snellen vision as one would expect. This research shows that there may be more important factors involved that limit the final visual outcome in DLEK. Correlation of the interface opacity with Snellen vision and wavefront analysis may be necessary to completely understand the visual post-DLEK aberrations.2714
German researchers offer support for using the femtosecond laser to create a safer, more precise and reliable method for both lamellar and penetrating keratoplasty compared to trephines. They created computer-controlled three-dimensional cuts in the corneal tissue of both donor and recipient. Laser pulses of 150-femtosecond duration and a repetition rate of 5 kHz are focused inside corneal tissue of porcine cadaver eyes. Within the focal plane each laser pulse causes a point-shaped micro cavity by photodisruption. They used a galvanometer scanner for precise 3-D positioning of pulses inside the cornea.
They report that size and the shape of the corneal transplant can be adjusted to individual needs, with different 3-D shapes to allow for simplified positioning and adapting the donor's transplant to the recipient eye. The femtosecond laser, they conclude, enables the surgeon to match the transplant more accurately with the recipient's eye.2700
A team of researchers from Wilmer and Thailand's Khon Kaen University describes a successful new technique using a blunt spatula and endothelium-side up orientation on an artificial anterior chamber to create posterior lamellar dissections without compromising endothelial cell number or planarity when compared to standard harvest.
They mounted eight human donor corneas onto an artificial anterior chamber and dissected deep stromal pockets. Four were mounted in the standard endothelial-side down and dissected using standard instruments [Group 1]. Another four corneas were mounted endothelial-side up and dissected using a flat spatula [Group 2]. Trephined lamellar graft thickness was assessed by ultrasound pachymetry. The grafts were also analyzed using vital staining of the endothelium and standard histological preparation. Group 1 achieved posterior graft thickness of 118 ±32 µm, with 0.86 ±1.48 percent devitalized endothelial cells. Group 2 achieved 92 ±23 µm thickness with 3.9 ±2.9 percent devitalized cells. The dissections using both harvesting techniques remained in plane and were smooth.2693
The reason for reduced final Snellen VA after DLEK, despite lower astigmatism, has been attributed to potential problems with interface opacity, posterior corneal vaulting, and higher-order wavefront aberrations. A group at the University of Iowa sought to determine if the use of automated microkeratome systems to create the donor lenticule produces a superior visual outcome in DLEK compared to manual dissection.
Thirty consecutive patients underwent DLEK. Eighteen had surgery using the Moria ALTK automated microkeratome, while 12 had surgery using the Bausch & Lomb artificial anterior chamber with manual dissection. Postoperatively, the mean best corrected Snellen VA, corneal topographic astigmatism, endothelial cell count, interface opacity, and higher-order wavefront aberrations were determined at one month, three months, and six months. The mean BCVA was 20/35 at three months and 20/32 at six months in the automated group and 20/55 and 20/51 respectively in the manual group. Corneal topographic cylinder was 3.06 D at three and 0.875 D at six months in the automated group and 3.478 D and 1.42 D respectively in the manual group. Early results show no significant difference in interface opacity, endothelial cell counts, or higher-order wavefront aberrations between the two methods. Their early results suggest that use of automated microkeratome systems may provide faster visual rehabilitation in DLEK as compared to manual systems. The inadvertent microkeratome complications which may occur should alert the surgeon to the fact that intraoperative pachymetry is important, as well as having access to various microkeratome head sizes so that the lenticule thickness may be adjusted in cases of thin donor buttons. 2691
A German group offers early findings suggesting that central corneal thickness seems to be correlated with body weight. In addition, anatomical features lead to lower peripheral corneal thickness values in the temporal and inferior than in the nasal and superior area. In the nasal and in the superior area the corneal thickness seems to decrease with age.
Using a Pentacam System, they investigated the influence of body size, body mass index, body weight, gender and refraction on central and peripheral corneal thickness. The Pentacam, a 180-degree, rotating, computer-aided Scheimpflug camera, may be used to generate reconstructions of the anterior segment from 12 to 50 single captures.
CCT was calculated from 25 single captures in the eyes of 182 normal Caucasian subjects (age: 18 to 83 years). The peripheral corneal thickness was measured within a 3-mm distance at 0, 90, 180 and 270 degrees.
The mean CCT of all 364 eyes was 534 ±36 µm, in the right and in the left eye (533 ±40 µm for females, 534 ±35 µm for males. Size, gender, age, height, body mass index and refraction produced no statistical influences on CCT values. The group calls for further trials to confirm these findings and to evaluate precision, reproducibility and independence of investigators of the corneal pachymetry with the Pentacam system, as well as with other pachymetry systems.2753
Pascal Dynamic Contour Tonometry (DCT) is a newly FDA-approved device that reportedly measures intraocular pressure independent of corneal thickness, corneal curvature and ocular rigidity. A Wills Eye group compared IOP in patients with keratoconus, pellucid marginal degeneration (PD) and unilateral penetrating keratoplasty (PK) for keratoconus or PD, measuring pressure by applanation tonometry, Tono-Pen tonometry and DCT.
They enrolled 21 eyes of 13 patients with KC, PD or PK with a mean age of 48.8 years. Twelve eyes had KC, eight eyes had a PK for KC and one eye had PD. Severity of ectasia was assessed by means of steepest curve by corneal topography and maximal thinning. For patients with the same diagnosis in both eyes, the more severely affected eye was included. DCT gave the highest IOP measurements followed by AT and TP respectively. The differences of mean IOP between Tono-Pen and DCT and Tono-Pen and applanation were statistically significant; the difference between applanation and DCT was not. They conclude that DCT may be helpful in IOP measurement in eyes with KC and PD, while Tono-Pen may underestimate the IOP.4954
Duke University researchers teamed with the company developing the instrument to test a new optical pachymeter that may overcome some of the drawbacks of ultrasound pachymeters. The new, non-contact instrument is based on common-path low-coherence spectral interferometry, which is of substantially simpler design and use than optical pachymeters based on scanning interferometry (such as is used in optical coherence tomography). With no moving parts and no dependence on precise positioning of the probe on the patient's eye, the pachymeter readily achieves handheld operation. It has 1-cm working distance from the probe tip to the cornea, a spot size of 18 µm on the cornea, and depth sampling resolution of 3.6 micrometers over a 3.25-mm scan depth range.
|
|
| Duke researchers are testing this instrument's capacity to provide rapid, non-contact, high-quality central corneal A-scans, enabling delineation of epithelial and corneal thickness. |
Disease
Better baseline BCVA, steeper corneas, corneal scarring, and fundus abnormalities are predictive of decreased VA in keratocones, according to the latest report from CLEK, the Collaborative Longitudinal Evaluation of Keratoconus Study, a long-term, observational study of 1,209 keratoconus patients.
CLEK uses seven years of follow-up from 953 subjects who had PK in neither eye at baseline and who provided enough data to compute the slope of the change over time in high- or low-contrast, best-corrected acuity. Subjects average 40.2 years old, 44.4 percent are female, and 71.9 percent are white. The slope of the change in high- (-0.29 ±1.5 letters/year) and low-contrast (-0.58 ± 1.7) best-corrected acuity over seven years translates into expected seven-year decreases of 2.03 high- and 4.06 low-contrast letters correct. High- and low-contrast decreases of Ž10 letters correct in at least one eye occurred in 19. percent and 30.8 percent of subjects, respectively. Significant, independent baseline predictors of reduced high-contrast, BCVA included better acuity, steeper first definite apical clearance lens (FDACL), corneal scarring, and fundus abnormalities. Significant, independent baseline predictors of reduced low-contrast, BCVA included better acuity, steeper FDACL, and corneal scarring. Each diopter of increase from baseline FDACL predicted an increased deterioration of 0.49 and 0.63 high- and low-contrast letters correct, respectively.4947
Investigators at Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, maker of the experimental VEGF Trap, say that systemic administration of VEGF Trap suppresses the development of corneal neovascularization, edema and inflammation following injury, even when delivered at low doses. They induced corneal neovascularization by alkali injury in mice. In a suture model, VEGF Trap was given subcutaneously at 1.0, 2.5 or 10 mg/kg on days 0, 4, 7 and 10 following injury, and the corneas were evaluated on day 13. In a chemical-injury model, VEGF Trap was administered at 12.5mg/kg subcutaneously on days five and 12 after chemical injury and the corneas were evaluated on days 42 and 70. For both studies, the vasculature was labeled by IV injection and the extent of neovascularization was quantified in corneal flat-mounts using the Scion Image program.
In the suture injury model, administration of VEGF Trap at all doses tested significantly inhibited corneal neovascularization compared to controls. Following chemical injury, delayed and transient treatment with the VEGF Trap (days 5 and 12) significantly decreased corneal neovascularization for at least 30 days following the last injection. Corneal edema and the infiltration of polymorphonucleocytes into the damaged corneas also were substantially reduced in VEGF Trap-treated animals compared to vehicle-treated controls.
At somewhat higher doses, treatment for a brief period following injury can exert relatively prolonged beneficial effects. Pharmacological inhibition of VEGF may be useful in the treatment of neovascularization and inflammation following corneal injury.4497
PDT with verteporfin is a safe and effective procedure to regress experimental CN and can be used to inhibit angiogenesis in the cornea, say researchers in the Republic of Korea. They induce CN by placing instrastromal sutures in the cornea of rabbits. One week after suturing, verteporfin was administrated intravenously and one hour later, 689 nm-laser was exposed on the right eye (treated group); the left eye was the control. PDT with verteporfin was then performed twice at one-week intervals.
One hour after the administration, fluorescent microscopy revealed vigorous fluorescence in the neovascular wall and interstitial tissue of the treated and control cornea. Following one session of PDT, mean percentages of the neovascular area in the treated group were 90.3 ±3.5 percent, and 96.4 percent in controls at three days; 71.6 percent and 88.6 percent at one week; and 43.6 percent and 76.8 percent at two weeks after treatment, respectively. Following two PDT treatments, mean percentages of the neovascular area was 86.6 percent in the treated group and 96.5 percent in controls at three days; 71 percent and 90.6 percent at one week, and 44.9 percent and 77.4 percent at two weeks after treatment, respectively. Histologic examination showed less sectioned neovascular area and number of vessels in treated eyes than in control eyes without histologic changes in iris.4499
Dr. Afshari is an assistant professor of ophthalmology in the Cornea and Refractive Surgery Service at the Duke University Eye Center.
*Reference numbers noted as footnotes correspond to the abstract numbers in the 2005 ARVO program.