The trend of recent years toward improved techniques and technologies related to corneal transplants shows no sign of slowing down, based on this year's ARVO abstracts. Also garnering attention is the potential of the anti-angiogenesis drug Avastin to treat neovascularization in the cornea. Here are some of the notable abstracts in these and other areas of corneal research. Unless specifically noted, these studies were not commercially supported.
Drug Issues
Certain Streptococcal isolates, particularly the S. viridans group, showed increased in vitro resistance to fluoroquinolones, with resistance rates almost doubling over a four-year period, say Bascom Palmer researchers.
The group compared in vitro susceptibility profiles of various Streptococcus isolates from 2002 to 2004 (earlier period) to those from 2004 to 2006 (later period) in order to assess for increasing fluoroquinolone resistance using Streptococcal isolates from keratitis, endophthalmitis, conjunctivitis, dacryoadenitis, blebitis and wound infections. Sensitivity profiles were obtained for Streptococcus viridans and Streptococcus pneumoniae to the fluoroquinolones available for testing. Among the 259 total cases, those with available fluoroquinolone sensitivity profiles (80 percent) were recorded. Fluoroquinolone sensitivity was determined using disk diffusion testing and by E-tests. Isolates were recorded as sensitive, intermediate or resistant. (The drugs were fourth-generation, and earlier, as available at the time studied.)
In the earlier period, there were 50 cases of S. pneumoniae, of which 100 percent were susceptible to the fluoroquinolones. Out of 42 cases of S. viridans in this period, four (9.5 percent) were resistant or had intermediate sensitivity to the fluoroquinolones. Of 71 cases of S. pneumoniae in the later period, two (2.9 percent) were resistant or had intermediate sensitivity to the fluoroquinolones. During the same time period, there were 53 cases of S. viridans, nine (17 percent) of which showed resistance or intermediate sensitivity to the fluoroquinolones.769
Minimal inhibitory concentrations are routinely measured for infectious keratitis to determine the susceptibility of inciting organisms to specific agents. How is in vitro antibiotic susceptibility associated with clinical outcomes in vivo? A group at the
Their double-masked clinical trial at Aravind randomized 42 patients with culture-confirmed bacterial keratitis to topical corticosteroid treatment or placebo. All study patients were to receive topical moxifloxacin treatment, although physicians were permitted to add or change antibiotics if necessary. Best-corrected visual acuity and infiltrate-scar size were measured. An average MIC for moxifloxacin was obtained from tests run on two separate days for each bacterial isolate using E-tests. A multiple linear regression model correcting for infiltrate-scar size at enrollment showed that every twofold dilution in MIC level was associated with a 0.25-mm increase in infiltrate-scar size at three weeks (p=0.052), and with a 0.32-mm increase at three months (p=0.03). No significant association was observed between MIC and logMAR visual acuity at three weeks (p=0.52) or three months (p=0.95). Moxifloxacin E-test reproducibility was high (intra-class correlation was 0.94). A higher MIC, they conclude, is associated with a larger final infiltrate-scar size but not with visual acuity. Limitations of this study include a modest sample size.4277
PKP Alternatives, Endothelial KP
Deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty is a reasonable alternative to penetrating keratoplasty, however safer insertion methods will be needed to increase long-term endothelial cell density, say surgeons in
At six months:
• The percentages of eyes that had 20/40 BSCVA or better were: 57 percent (4/7 eyes) in 9-mm DLEK, 64 percent (36/56) in 5-8 mm DLEK; and 44 percent (4/9) in PK conversion.
• The mean CT astigmatism was: 1.41 ±0.60 D in 9-mm; 1.94 ±1.46 D in 5- to 8-mm; and 4.29 ±2 D in PK conversion. The two DLEK groups showed a 25 to 37 percent reduction in CT astigmatism compared to the preoperative state, while the PK conversion group showed a 45-percent increase in astigmatism.
• The average ECD was: 2,400 ±393 in 9-mm, or a 24-percent loss compared to preop; 1,710 ±454 cells/mm2 in 5-mm, or a 44-percent loss; and 2432 ±310 cells/mm2 in PK conversion, or a 24-percent loss.
The most concerning issue in this study, the authors say, is the decrease in ECD after small-incision DLEK. Folding of the donor tissue prior to insertion has a detrimental effect on the ECD after DLEK. Folding of the tissue, they suggest, may stimulate a certain population of corneal endothelial cells to undergo apoptosis, which becomes evident by six months after DLEK.4712
Emory
The four group results:
• Group 1, preparation of the donor button on the Moria artificial chamber and ALTK system; average endothelial cell loss: 17.1 percent.
• Group 2 added the steps of folding the prepared donor tissue with viscoelastic and grasping the tissue with non-compression Rossenwasser forceps; average cell loss: 16.4 percent.
• Group 3 included folding with insertion of the tissue using compression forceps and simulation of endothelial touch with chamber shallowing; average cell loss: 54.1 percent.
• Group 4 included simulation of a 10-minute air bubble; average cell loss: 18.8 percent. The most significant amount of endothelial cell loss occurred with use of compression forceps along with the tissue insertion step.
The marked endothelial cell loss could account for higher primary graft failure rates in DSAEK compared to penetrating keratoplasty. Small incision insertion and compression forceps increase the amount of endothelial cell loss with the procedure.1131
Is DSAEK with cataract surgery any riskier than DSAEK alone? Researchers in
Combining cataract surgery with DSAEK in the new "triple procedure" does not increase the risk of dislocation, nor does it increase measured endothelial cell loss at six months, they conclude.1132
Patients may reject their donor cornea even if they do not show classic rejection patterns on exam or are completely asymptomatic in their history, based on an
The retrospective, interventional chart review evaluated patients with previous DSEK who developed immunologic graft rejection. Of 601 DSEK cases, 477 were seen postoperatively at one or more time points between one and 30 months. Graft rejection was seen in 26 patients, four of which had bilateral rejections that presented at either the same or different times. The mean time from surgery to diagnosis of rejection was 228 days (SD 141; range: 29 to 496). The most common findings were decreased visual acuity, irritation and presence of keratoprecipitates (KP). Of the 30 eyes reviewed: 10 were asymptomatic; 23 had KP; 11 were edematous; five had both edema and KP; 16 had documented decreased VA; 14 were irritated; and eight appeared injected. In contrast to full-thickness grafts there were no epithelial immunologic reactions because the epithelium is not transplanted in DSEK. No endothelial rejection lines were observed.4720
A University of Tennessee, Memphis, pilot study describes the morphologic features of the posterior stroma following deep lamellar flaps fashioned by the femtosecond laser versus microkeratome and compares these findings to the morphology of Descemet's stripping.
Six eye bank corneoscleral buttons were used. On three buttons, the femtosecond laser (IntraLase) was used to create anterior flaps of 400-µm thickness. The laser cuts were made with an energy level of 4.0 µJ with a spot separation of 6 µm, in three different laser patterns: spiral; raster; and spiral plus raster. Microkeratome flaps were performed on two buttons with a Moria LSK-1 with a 250-µm head size. Three laser-cut specimens, one microkeratome-cut specimen and one Descemet's-stripping specimen were examined by scanning electron microscopy.
The side cuts of the stroma with the laser were very uniform and formed about 90 degrees to the base of the flap, while the side cut of the microkeratome flap was sloped and irregular. In contrast the stromal bed of the microkeratome- produced flap was smooth and more regular when compared to all of the laser cuts. Among the laser cuts, the stromal bed fibers produced with raster mode had a more haphazard, jagged appearance than that produced in the spiral mode. The stromal bed fibers produced with both raster and spiral modes had a similar appearance as those produced with the spiral only mode.
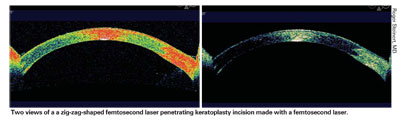
Two views of a zig-zag-shaped femtosecond laser penetrating keratoplasty incision made with a femtosecond laser.
Roger Steinert, MD
The stromal bed surface in femtosecond laser deep lamellar cuts is more irregular than that produced with mechanical microkeratome, they conclude. The irregular surface may have different implications for the visual performance of posterior lamellar procedures than that for anterior lamellar procedures.4698
University of California, Irvine, researchers (one of whom reports commercial support from IntraLase) conclude that short-term results support the technical feasibility of using a zig-zag shaped femtosecond laser penetrating keratoplasty incision, and the technique may improve the speed of recovery and overall quality of optical results. Using an IntraLase with modified hardware and software, they created zig-zag-shaped (0.5 mm lamellar ring at 320 µm depth, connected by 45 degree-angle side cuts to the anterior and posterior surfaces) incisions on patients undergoing full-thickness PKP. As of November 2006, 16 eyes had reached one to nine months follow-up. Orbscan topography was obtainable as early as postoperative day one on seven eyes because of the high degree of immediate corneal surface regularity. For eight eyes with topography at three months, the mean simulated K reading was 3.5 D. Six of eight eyes were at or below the mean, with a range of 0.4 to 8.4 D prior to any suture adjustment. Macular disease in most patients precluded meaningful visual acuity data. One patient with rapid suture loosening and subsequent suture breakage had full suture removal by three months, with 2.3 D of regular astigmatism and no evidence of wound dehiscence. They conclude that the zig-zag configuration is biomechanically stable and secure. A study with a larger series and a control group is in progress.4706
Other Surgical Issues
Treatment that combines riboflavin and ultraviolet A-induced collagen cross-linking followed by surface excimer ablation may offer effective visual rehabilitation in keratoconus. Surgeons in
In all treated eyes, the progression of keratoconus appeared to stabilize. Visual acuity, both UCVA (20/400 to 20/50) and BSCVA (20/100 to 20/30) improved drastically. There was a reduction in spherical equivalent of 7.4 D. Endothelial cell count was unchanged. Mean keratometry changed from 55 to 47.5 D. Pachymetry decreased from 420 to 390 µm. Long-term results are necessary to evaluate the duration of effectiveness and to exclude long term side effects, the authors say.5324
A large, retrospective chart review at the
Of 146 PKP procedures included, 31 eyes (21.1 percent) had history of glaucoma or were on anti-glaucoma medication before surgery, and six eyes (3.5 percent) presented with high IOP (>20 mmHg by Goldmann applanation) on the day of admission. After surgery, 70 eyes (47.9 percent) had IOP of 21 mmHg or more (mean 27.15 ±5.66; range 21 to 49). The increase in IOP appeared after a mean postop period of 73 ±135 days, and continued for an average period of 16.4 ±17.7 days. Although the increased IOP was controlled in most patients, 35 eyes (23.9 percent) had a second episode of IOP elevation 212.2 ±276.7 days after surgery.
Multivariate analysis revealed that preexisting glaucoma (p≤0.003) and an additional intraocular surgery combined with PK (p≤0.01) were the main factors predicting high IOP after PK. Age, gender, indication for keratoplasty, graft size, type of sutures and immediate postop IOP rise were not significant predictors. In 11 eyes (7.53 percent) the topical anti-glaucoma therapy failed, and three of them required glaucoma filtering surgery. Nine of 13 failed grafts occurred in eyes with postoperative IOP elevation, but this was not significant (p=0.107). Nor did preexisting glaucoma have a significant effect on graft failure (p=0.219). Ocular hypertension did not have an adverse effect on graft survival.4676
A retrospective analysis at Lackland Air Force Base,
A combined Swiss-Italian study suggests that the use of mean pupillary power, as measured in corneal topography, can substantially increase the predictability of postoperative refraction after IOL implantation in eyes with pathological corneas. The researchers calculated IOL power using standard keratometry (four measurement points) and topographic mean pupillary power (about 4,000 real data points) in five different types of pathological corneas. Normal corneas served as controls. IOLs were selected on the basis of plugging the mean pupillary power into the IOL power calculation formula. A separate calculation was made with the standard keratometry values. The two predicted refractions were then compared with the effective postoperative refraction obtained to determine which IOL power came closest to the intended refraction.
In normal corneas (and normal axial lengths), the IOL power differences between the two methods were on average within 0.5 D, although they ranged up to 1.5 D. Abnormally steep corneas' differences were as much as 3 D from recommended IOL power; irregular astigmatism was up to 3.5 D; keratoconus up to 18 D; pellucid marginal degeneration up to 2.5 D; and post-corneal refractive surgery ranged from 1.5 D to 6.5 D. (Topography maps will be used to illustrate each of these categories of pathological corneas.) In all eyes the IOL power obtained from the formula using the mean pupillary power gave a significantly closer approximation of the intended postoperative refraction than did keratometry values.3528
Animal model testing suggests that a cellulose derived from a Gluconobacter xylinoides subspecies may serve as a wound dressing for corneal surface injuries. Researchers in
The microbial cellulose grafts caused no observable discomfort to the rabbits. The rabbits re-epithelialized, as measured by no evidence of fluorescein staining, within 24 hours of grafting. Corneas were clear and compact. Rabbits gave no indications of discomfort throughout the 24-hour time-course, and in two instances the grafts appeared to have dissolved. These findings, the authors report, are consistent with other on-going studies involving cutaneous wounds, in which wound closure occurred at a significantly greater rate of healing in contrast to other standard-of-care treatments.787
Dry Eye, Tears
What's the most effective way to differentiate chronic blepharitis from dry eye? Investigators in
They assessed a range of tear physiology measures, including tear turnover, evaporation, structure, volume and osmolarity and meibomian gland dysfunction, in 19 patients with chronic blepharitis and 41 with dry eye. No significant differences or distinct cut-offs were seen in any of these except MGD score. MGD score (with a cut-off value of two dysfunctioning glands) was found to be useful to differentiate blepharitis from dry eye with sensitivity of 79 percent, specificity of 69 percent, positive predictive value of 60 percent, negative predictive value of 85 percent, and overall accuracy of 62 percent. Series and parallel combinations of tests were not found to be more effective in the differential diagnosis of these conditions. Discriminant function analysis was also applied but it removed all the parameters, except MGD scores, from the discriminant function.412
Just 20 minutes of continuous near work may significantly destabilize the tear film and increase dry-eye symptoms, say
S-TBUD decreased in 20 (67 percent) and TBUT in 22 (70 percent) Individual measures that increased significantly after the near task included the AB after 5 sec, the final AB (DE only), and the symptoms of discomfort and burning (p<0.05). However, dry-eye subjects were significantly more symptomatic than controls both before and after performing the near task (p<0.003). TBUT correlated with S-TBUD measures (AB, slope, MBI), and the AB at 5 seconds correlated with the symptom of discomfort (p<0.003).
After performing the near task, subjects showed substantially accelerated tear breakup in only 5 seconds, which may increase the risk for ocular surface exposure if the average blink rate is 12 per minute (once every 5 seconds).417
Most dry-eye patients who use topical cyclosporine 0.05% (Restasis) twice a day for at least a year and achieve control of their symptoms can maintain suppression of disease and possibly show improvement after decreasing to once-daily. Allergan-affiliated researchers in
At six months, patients on cyclosporine q.d. demonstrated statistically significant improvement in TBUT (4.13 seconds [n=37] vs. 3.11 seconds at baseline [n=50]; p=0.0003) and lissamine-green staining (4.42 [n=37] vs. 6.51 at baseline [n=50]; p=0.024). Fluorescein staining, Schirmer's and OSDI were not significantly different from baseline (p> 0.05). At the conclusion of the study, OSDI was significantly superior in the q.d. group compared to the b.i.d. group (15.91 [n=37] vs. 22.62 [n=48], p<0.05). The other outcome measures between q.d. and b.i.d. were not significantly different (p>0.05). Seven out of 50 patients (14 percent) in the q.d. group (versus 0 in the b.i.d. group) ended the study early due to lack of efficacy (p<0.05), and all went back to b.i.d. dosing.374
Anti-Angiogenesis in the Cornea
Bevacizumab (Avastin), approved as anti-angiogenic treatment for cancer, has drawn great interest in the retina community for its potential in treatment of choroidal neovascularization. The level of interest in the drug's ability to inhibit corneal neovascularization is also high and growing.
A group at the Mayo Clinic,
A group at the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, looked at the effects of subconjunctival bevacizumab in corneal neovascularization. Five patients with acute or chronic corneal neovascularization in the setting of graft rejection in PKP (n=2), lamellar keratoplasty (n=1), neurotrophic keratitis (n=1), and KID syndrome (n=1) were given one to four subconjunctival injections of 1.25 mg bevacizumab in 0.01 cc diluent adjacent to the site of neovascular pannus. Patients were then followed (mean four months) to document the effects on corneal neovascularization and visual acuity. Improvement in neovascularization (partial regression of vessels or the presence of ghost vessels) and ≥1 line gain
A small study at the University of Erlangen-Nurnberg in
Four patients (six eyes) with corneal neovascularization received 5 mg/ml topical bevacizumab treatment over eight months.
All patients receiving topical bevacizumab treatment showed improvements in VA and regression of neovascularization. One patient (one eye) developed a descemetocele five months after treatment, but the remaining three patients (five eyes) showed no serious drug-related ocular or systemic adverse events during follow-up. While the long-term efficacy of local bevacizumab treatment remains unknown, this treatment principle may be a new effective way to treat neovascularization in patients with limbal stem cell insufficiency, say the authors.1718
Investigators at the Federal University of Sao Paulo, Brazil, found that bevacizumab does affect angiogenesis, but not metalloproteinase activity to a significant degree. They used silver nitrate to chemically cauterize the corneas of four groups of rats. A control group received a subconjunctival injection of 0.02 ml of 0.9% saline solution; Group 0 received 0.02 ml of bevacizumab just after the injury; Group 3 received the same treatment at three days; and Group 5, the same at five days. After euthanization at seven days, new vessels were photographed and analyzed by a computerized system. Metalloproteinase (MMP-2 and MMP-9) activity was evaluated by zymography.
The percentages of neovascularization coverage of the corneal surfaces were: 53.56 percent ±15.11 (mean ±SD) in the control group; 35.57 percent ±18.80 in G0 group; 30.60 percent ±11.82 in Group 3; and 35.86 percent ±0.07 in Group 5. Zymography showed a slight reduction in MMP activity when bevacizumab was administrated at the moment of injury and the most significant reduction at day three. At day five, there was an increase in metalloproteinase activity. Angiogenesis was inhibited in all treated groups. There were no statistical differences in vascular density among them. MMP activity was decreased, but not at significant levels, demanding more investigations regarding the interaction of bevacizumab and MMP activity.1701
Topical administration of VEGF Trap inhibits corneal NV and inflammation following suture injury, according to investigators at Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, which manufactures the product. The group induced corneal NV in 30 anesthetized adult mice by intrastromal placement of three nylon sutures. They administered VEGF Trap, a receptor-based fusion protein that binds all isoforms of VEGF-A, topically as a 4 mcL drop at concentrations of 100, 10, and 1 mg/mL three times a day beginning immediately after injury. Control animals received vehicle eye drops or drops containing 10 mg/mL of a control protein on the same schedule. At nine days, the corneal vasculature was labeled by intravenous injection of fluorescein conjugated lycopersicon esculentum lectin, and the extent of NV was evaluated post-mortem in corneal flat-mounts. The Scion Image program was used to measure the length of corneal neovessels.
Topical administration of VEGF Trap significantly suppressed corneal NV (98.4 percent inhibition at a concentration of 100 mg/mL compared with the vehicle-treated group; 80.6 percent inhibition at 10 mg/mL compared with the protein-treated group; treatment at 1 mg/mL showed only a slight, non-significant reduction in neovascularization). VEGF Trap treatment also markedly reduced injury-induced inflammation. No free VEGF Trap was detected in the serum following nine days of administration (limit of detection, 18.4 ng/mL), and no detectable systemic exposure to active drug was found, even at the highest dose tested.1710
Dr. Afshari is an associate professor of ophthalmology in the Cornea and Refractive Surgery service at



